An Internet address or domain name is the equivalent of your mailing address on the Internet. It’s how your contacts and customers will find your website on the web. A domain name is therefore essential when creating a website. An Internet address consists of a “www” (world wide web) prefix and a domain name. This domain name is itself composed of a character string and an extension (TLD – Top Level Domain).
Below, you one will see an example of a domain name.
www.example.com
In this domain name example, the “www” part means the World Wide Web. “com” is the Top Level Domain (TLD) part. In between, “example” is the part of the domain name that is specific to the website.
The main part of the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is the domain name. This indicates where a resource can be found within the Domain Name System (DNS). The conversion of domain names to an IP Address is handled by the Domain Name System. Every website has a Domain Name and an IP Address. The name of the website, the IP Address is unique to it. In the Domain Name System, a domain is presented to the user on the Web Server by finding an equivalent IP Address. This process resembles a telephone address book. You cannot remember the numbers of people even if you remember their names. When you search for the person’s name on your phone, you are also looking for their phone number. Likewise, when you enter the Domain Name in the address bar of the browser, after the DNS Lookup and DNS Reverse Lookup processes, a request is made to the IP Address.
Each web server is identified by an IP Address. IP Addresses are divided into IPv4 and IPv6. Human users often do not see these numbers. A sample IP Address is below.
192.125.211.23.
Since it is difficult to remember such a number and it is also difficult to write it in the same way, an alhpanumeric method was created.
What are the parts of a domain name?
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) refers to the exact location of a domain within the DNS System. FQDN consists of two parts. Below is an example of an FQDN.
mailserver.example.com.
The “mail-server” section refers to the hostname. The “Eample.com” section shows the domain under which the hostname is. Thanks to the domain name, it connects to the computer containing the IP Address and then the webserver. Thus, the contents, transactions, and assets related to the “mail-server” are requested from the webserver by the user. “www” is often used as a hostname for domain names.
www.example.com.
Root Label is the last section for Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). FQDN is always a “.” ends with. This last point is not used during internet use in everyday life. The last point, the Root Label, indicates that internet addresses are always in a hierarchy and are a breakdown to the very end.
| Third level domain | Second level domain | Top-level domain | Root label |
| www | .example | .com | (empty) |
Sağdan sola doğru, bir FQDN şunlardan oluşur:
- Root-label,
- Top-level Domain (TLD)
- Second Level Domain (SLD)
- Third-level Domain,
In theory, “www.example.com” is equivalent of the “www.example.com.”.
Root Label Part of Fully Qualified Domain Name
The first step of the FQDN is the “root label”. In some sources, Root Label is also called “Null Label”. Often, Root Label is not used in daily internet life and is left blank. However, in any case, it can be used if desired.
Root Label is a useful concept for understanding the Domain Name System Root-tree structure.
“www.holisticseo.digital.” is the FQDN version of the “www.holisticseo.digital”.
Top-level Domain (TLD) Part of the Fully Qualified Domain Name
The top point of Name Resolution is the Top-Level Domain. The main reason for this is that the Root Domain or Root Label of Domain is not used mostly in internet usage. Top Level Domains (TLDs) are operated by the Network Information Centers (NIC). Network Information Centers (NIC) include name servers, recording of the second-level domains that are under the Top Level Domains. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a sub-organization that works under the Internet Cooperation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). IANA makes a distinction between two different Top-level Domains such as Country-code Top Level Domains and Generic Top-level Domains. “.info”, “.com”, “.net” or “.org” are the Generic Top Level Domains while the “.de”, “.tr”, “.uk”, “.us” are the Country- code Top Level Domains.
Also, there are Sponsored Top Level Domains such as “.edu”, “.mil”, “.gov”. Sponsored Top Level Domains are sponsored by the state cooperations or governmental institutions. Country-code Top-Level Domains and Sponsored Top Level Domains are can be used with certain conditions. To use a Country-code Top Level Domains, having a residenecy, citizenship and some other official documents are necessary. To use a Sponsored Top Level Domains, being a govermental, educational or state cooperation is necessary.
Top Level Domains exist at the end of the domain, that’s why they are called “domain ending”. In Holistic SEO & Digital, the “.digital” is the Top Level Domain. To perform the registration for certain Country-code Top Level Domains, there are special Network Information Centers for some countries.

Second Level Domain (SLD) of the Fully Qualified Domain Name
The most generic and unique part of the domain is the Second Level Domain (SLD). Second Level Domain or the Actual Name of the Domain are also brand names. In “www.holisticseo.digital” address, the “holisticseo” is the Second-Level Domain.
A Second Level Domain is always under a Top-Level Domain. A Private Domain Name Registrar that works with the permission of related Network Information Center (NIC) can sell the Second Level Domain to persons.
Third Level Domain Part of the Fully Qualified Domain Name
Third Level Domains are actually the sub-addresses of a domain. Third Level Domain is a separate, distinct section of the web site. Most of the Third Level Domains are also “subdomains” but the “subdomain” term is also being used for the marketing terminology. For instance, “mailserver.example.com” is actually the “subdomain” of the “example.com”. But, it is only being used for the “emailing” activities under that domain address. In this context, this subdomain is not related to the “generic marketing strategy”.
Third Level Domains have a distinc category profile such as different landing pages, services, servers.
The common names used for the Third-Level Domains are “m” for mobile servers, “mail”, IMAP or “pop3” for the mail servers, country codes for local versions of the same web site.
Below, you will see Third-Level Domain Variations for the Wikipedia.
| Third level domain | Second level domain | Top-level domain | The special path on the server |
| fr | wikipedia | org | /wiki/Main_Page |
| tr | wikipedia | org | /wiki/Anasayfa |
Every different language version of Wikipedia serves the equivalent versions of the same web pages. But, also in this example, there is a unique side. Every different language version of the same web page under Wikipedia is also being written by different writers with different sources, attributions, and angles. In this context, we can’t call these “Third-Level Domains” as symmetric equivalents.
But, in most examples, Third-Level Domains are also being used with “hreflang attributes” for showing that the web pages from different languages are symmetric equivalents of each other.
Third-level domains are often referred to as “subdomains”. Strictly speaking, however, this term cannot be restricted to third-level domains.
Country-code Top-Level Domain Part of the Fully Qualified Domain Name
The end of a web address consists of a Top-Level Domain. Country Code Top Level Domains are the last part of web addresses specific to a particular country. In addition, there are Country-code Top-Level Domains specific to a specific region, even if not a country. For example, “.eu” is an example of Country-code Top Level Domain (ccTLD) for the European Union. “.asia” is for the Pacific Region and Asia. “.tr” is an example of ccTLD for Turkey. Which ccTLD will belong to which region is determined entirely by the Internet Cooperation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). Registration of different domain names under ccTLD is managed by the relevant Network Information Center (NIC).
Commercial activities performed to register different domain names under ccTLD are managed by end-user and Domain Name Registrator. Domain Name Registration gets operating permission from the relevant Network Information Center. In total, there are over 200 ccTLD instances. Some countries have country-specific Network Information Centers for ccTLD registration. For example, only “DENIC” can be used for Germany.
To learn more about Country-code Top Level Domain, you can read our related guideline.
Characteristics of ccTLDs
Country-specific domain endings usually refer to the region or language area to which the content of an online presence is directed. Country-specific top-level domains always consist of two letters from the Latin alphabet.
Country-specific Domainler veya Country-code Top Level Domainler her zaman Latin Alfabesinden iki harften oluşur. Farklı bir dil, bir ülke veya bir bölge için ccTLD’ler mevcuttur.
Latin Alfabesi ile başlamayan veya sadece Latin Alfabesinden iki harf içermeyen ccTLD örnekleri mevcuttur. Az sayıdaki bu örnek, IDN-ccTLD olarak çağrılır. IDN-ccTLD or Internationalized Country Code Top Level Domains exist in Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka has “lk” as its cc-TLD but also it has “.ලංකා/.இலங்கை” ccTLDs that are special to the island nations in Sinhala and Tamil languages.
Sponsored Top Level Domain (sTLD) Part of the Fully Qualified Domain Name
Sponsored Top-Level Domains are being used for special communities, institutions, and corporations. Usually, Sponsored Top Level Domain (sTLD) is used by governmental or state institutions or educational organizations such as universities, military institutions, and state cooperations. “.edu” for universities, “.gov” for government institutions or “.mil” for U.S Military institutions are being used as Sponsored Top Level Domains. “.asia” domain extension is a Sponsored Top-level Domain while it is also a “Country-code Top Level Domain”. Because “.asia” is only for a region while it is being sponsored by “DotAsia Organization”.
How Does a Domain Work?
A Domain Name work through Domain Name System (DNS). When the one enters a domain name into the browser’s address bar, the browser requests the web site from the Domain Name Server that stores the Domain. A Domain Name Server works in a Domain Name System. You may see an example of a domain name server from Namecheap Hosting Provider.
- ns1.namecheap.com
- ns2.namecheap.com
Below, you will also sea an example of Domain Name Server from the BlueHost Hosting Provider.
- ns1.bluehost.com
- ns2.bluehost.com
Usually, hosting providers provide two different name servers for a website in case of one of the name servers do not work, so that the one can access the web site.
All of these name servers are actually computers that run a program in the server such as Apache or Nginx. Apache and Nginx are the programs that are popular in the web servers. When the user enters the domain name into the browsers’ address bar, the browser requests the web site from the Domain Name Server and Web Server. Domain Name Server serves the web site through these types of server programs to the user through the domain name.
For SEO, Domain Name System (DNS) Lookup is an important term. You also may read, how to perform DNS Reverse Lookup via Python Guideline.
Who is Responsible for the Domain Name System?
The acronym ICANN stands for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) was founded in 1998 by an amalgamation of different interest groups – in addition to business, technology, and science, users were already on board back then. ICANN forms a kind of superstructure for the previously responsible IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), which had worked on behalf of the US government. The IANA remained as a subgroup of ICANN and is still directly subordinate to the US Department of Commerce.
The foundation was based on a proposal by the US Department of Commerce to found a new non-profit organization to administer the system of Internet names and addresses and to take over the technical management of the domain name system.
With ICANN, now based in Los Angeles, a non-profit organization was finally created that sets the rules for a significant part of the Internet. Contrary to what many people think, ICANN is not an international organization formed by states, but a private foundation subject to California law.
How to Choose a Domain Name?
Before you get a domain , you should consider a few points. Otherwise you could incur higher costs or unknowingly commit a crime.
- In principle, every person and every company or organization can buy their own domain. Only certain endings, the Top Level Domains (TLD), are linked to certain conditions.
- In most cases, the provider will offer you the desired domain query. You can enter your desired domain name there and see a selection of TLDs, provided the domain is still available.
- It is possible to buy a domain that has already been used, these are usually significantly more expensive and, in case of doubt, may have already been banned by Google. Therefore, you should do a Google check in advance. If the website does not appear, you should stay away from it. In addition, there is a transfer fee to be paid by your domain dealer.
- As a company, in particular, you should make sure that you have the option to expand the TLD after the purchase. You buy the domain example.de and later want to reach the Austrian market with example.at. This option should be open to you. Check the availability of the domains in advance.
- Pay close attention to the term and extension. With some providers, the price conditions can skyrocket after the first year. Take a close look at the providers.
- A domain also includes web hosting, technical support, email facilities, and so on. This should either be included directly in the contract or you should include it in the total costs.
- Make sure you avoid trademark and copyright infringement. If you choose a name that is very similar to a brand, that domain could be revoked from you.
- The domain name will become the brand name of the web site, including generic terms and brandable, memorable terms are important for SEO and Branding.
- Using a “.com” Top Level Domain can be better for a brand since it is being perceived as a canonical extension by most of the users.
- Using an easy to pronounce and remember domain name is better for branding.
- Shorter URLs and shorter Domain Names are better for Page Loading Timing since they decrease the URL character count site-wide, but also they are easy to type, and remember.
- Including “hyphens” and “numbers” in the domain name are usually harmful to the branding. Try to avoid them while choosing a domain name.

How to Sell a Domain Name?
There are different ways to sell a domain. For example, you can put a visible notice on the home page of the domain – a kind of “for sale” sign. Interested parties can contact you directly to discuss the sale of the domain with you. Other domain dealers are successful on eBay. The auction platform offers a good and well-known infrastructure. If you choose to trade domains on eBay, you will have access to the same functions that you know from other types of products.
But there are also sites that you can use specifically to buy and sell domains. Platforms like Sedo or Flippa provide marketplaces on which you can offer your domain. Such platforms are also important if you want to get into domain trading – i.e. not just want to sell a domain that is now unused, but also specifically looks for valuable domains in order to then sell them profitably.
Can I Move My Website to a Different Domain Name?
A domain name can be moved to another domain with domain-based 301 Redirections and a new domain can be pointed to the hosting server. This process is being called Site Migration. To migrate a web site, 301 Redirections should be adjusted for the relevant URLs. Every URL should be redirected to the equivalent new version of it. During a site migration, from Google Search Console and also Bing Webmaster Tools, the site owners should declare that the web site is being moved. This way, the web site’s indexed page’s addresses will be changed with the new web pages. From Google Search Console Performance Report or Bing Webmaster Performance Report, the site migration process should be watched. Also, log file analysis will help SEOs to see how the migration process is being performed.
What is Domain Privacy? Do You Need Domain Privacy?
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) has the physical address, phone number, e-mail address, and name information of the domain name owners. Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) publish all of the domain-owners information on the internet for creating a public and transparent internet environment. Domain registrars who want to hide their personal information on the internet use an add-on service that is called “Domain Privacy”. In this way, ICANN can’t show the personal information of the domain owner.
Having a transparent profile on the ICANN can help the Search Engine Algorithms to see who is the owner of the web site, is the one reliable or shady? Is the one an expert or just an entrepreneur? These types of information can help an Entity-based Search Engine to understand the web site’s reliability. Having an open and transparent ICANN Domain Owner Information is better for SEO. But, if the one is sensitive about privacy, then using Domain Privacy is a valid option. In addition to these, usually, the Domain Registrator’s private information can be seen in the WHOIS.
Can I Buy More Than One Domain?
Yes, anyone can buy as many as domain they want to buy.
Can I Cancel My Registration of a Domain Name?
Most of the domain registrars do not let their customers cancel their domain registration. Some of the domain registrars let customers cancel their domain name registration. In the case of cancellation of the domain name registration, most of the domain name registrars do not have a refund policy. But some of the Domain Registration Platforms refund the domain price over the rest of the time of the registration contract. After the domain name registration cancelation, the domain name will be open to registration for others.
What is the Difference Between a Domain, Hosting, and Website?
The website is a document created with different software languages such as HTML, Javascript, CSS. Hosting is the database where the created website lives and is presented to the client. The domain is the name used by the hosting to present the website in question to the user and to direct the client to the website in question.
Therefore, both a hosting and a website are required to create a website. Then, by selecting the domain name, the function of the website, the company name and identity, and the website are accessed and defined.
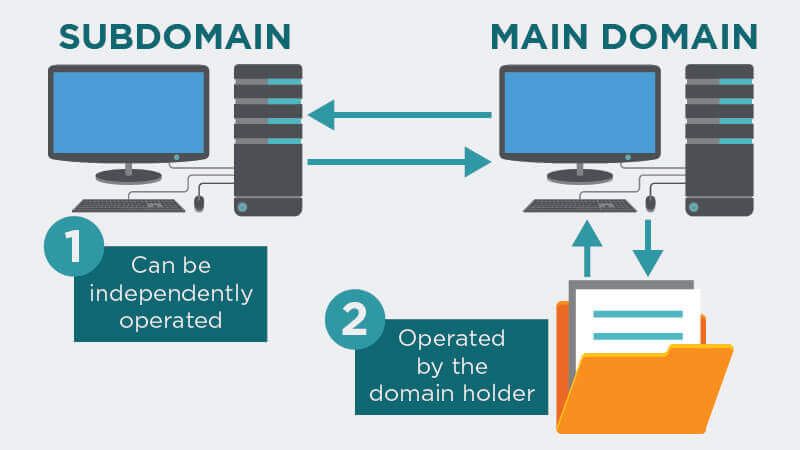
What is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is a domain that is located below another domain in the DNS hierarchy. So basically every domain below the TLD is a subdomain. While the Sub-level Domain (SLD) is a subdomain of the Top-level Domain (TLD) in the domain structure, the third-level domain is subordinate to the SLD as a subdomain. Subdomains bring advantages primarily through the logical structure of a domain. As the example of the online encyclopedia Wikipedia shows, the third-level domain is of particular importance here. In principle, however, subdomains below the third level are also possible. Subdomain has slight differences from the third-part of the domain as it is said before.
Last Thoughts on Domain and Holistic SEO
Domain Name, DNS Lookup, DNS Reverse Lookup, Server Response Times, IP Address, Domain Name System, Web Server, Apache, Nginx, Top Level Domain, Country Code Top Level Domain, Sponsored Top Level Domain, and Subdomains are the important terms for the Holistic SEOs. Knowing these terms, their meanings and effects on the web are important to create an SEO and Digital Marketing Strategy. Domain Names do not have a heavy effect on the Rankings for the Google Search Engine like in the old days, but despite the official statements, the one can observe some ranking and query profile relations with the domain name. Also, despite Google’s and other Search Engine’ statements, there are minor relations between a domain name and query relevance for ranking some terms. Using a brandable domain name that includes the generic terms with a natural blending can be better.
Knowing how to choose the right domain name or how to find the correct domain name, where to buy a domain, or how to reach a domain’s owner, knowing the relationship between these technologic terms and the technology behind them is important for improving a Holistic SEO Vision.
Our Domain Name Guideline will be improved by time.
- Sliding Window - August 12, 2024
- B2P Marketing: How it Works, Benefits, and Strategies - April 26, 2024
- SEO for Casino Websites: A SEO Case Study for the Bet and Gamble Industry - February 5, 2024