Semantic SEO is to create a content network in a relevant and meaningful structure for each entity within a subject. Semantic SEO is connecting terms, entities, facts to each other within a factual accuracy and relational relevance. By focusing on meanings and topics instead of words, it has the purpose of satisfying the search intent of the user better and being the authority for the Search Engine and the User on a particular subject. Google is a Semantic Search Engine that creates connections between entities, searches intents and organizes the information on the web. Thus, creating an already organized content structure with clearly connected entities is important for Semantic Search Engine and Semantic SEO.
What is the difference of Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO does not aim to answer a single question about a subject, but to answer all the questions that the user may need and belong to the same topic and to present the necessary information in a hierarchical structure.
Thus, as more possible search-intents are met, more authoritative and comprehensive pages are created on the same topic. With Semantic SEO, complete, comprehensive, and guideline content is created. These contents can also have various web applications, visual and video content, text content or surveys, PDF Files that meet the needs of the user. Different parts of the same topic are placed in a hierarchy on both page URLs and Breadcrumb, internal links, header, and footer links, thus creating a firm specialized in a subject.
Semantic SEO offers an organized user-journey experience, as opposed to randomly generated individual content. As a result of specializing in a single vertical, Google, Bing, Yandex, or other Search Engines will over time be sure that the user finds content that matches the search intent for a particular topic. With the authority provided by Historical Data and the wide query profile, the company may gain more comfortable ranking and brand awareness in the same and connected subject networks.
How to Write Content Using Semantic SEO
Semantic Content Writing is the term for content creation for Semantic SEO Principle. In order to write content suitable for Semantic SEO, all queries performed by the user, all subheadings about a topic are placed in a hierarchy. For the Semantic SEO project, SERP scanning and Search Intent definition should be made according to all subtopics within a subject. Search volumes are also important in the content network to be created for Semantic SEO. You can follow the steps below for Semantic SEO Strategy.
- The queries used to investigate the topic should be listed hierarchically.
- The search-intent of these queries should be analyzed.
- Entities such as persons, institutions, laws, countries, places, cities, and dates in the subject should be listed.
- How much separate contents will be created on the subject should be determined.
- The hierarchy in which the contents will be linked to each other and how to link with which anchor texts should be determined.
- In order for the contents to be completely distinguishable from each other by Search Engine, it should be determined how much of which subject will be processed in which content.
- It should be specified to the Search Engine with the meta tags, headings, keywords, and anchor texts of the URLs to be created, which content meets which Search Intent.
- Main Content and Supplementary Content half in a URL should be done properly to avoid the Keyword Cannibilization problem.
- The Layout, Functions, and Contents of competitor pages in the SERP of the most important queries and the historical ranking results in these queries should be examined.
- The content should be created in a fully specialized language, to benefit the user and making sure that it is easily understood by the Search Engine.
How to Perform Keyword Research for Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is an important concept as it allows focusing on an entire topic rather than a single keyword. For this reason, keyword research studies also differ. At this point, instead of focusing on one query, many queries that are interconnected should be focused on.
The following steps should be followed for Semantic SEO Keyword Research.
- All of the tools such as Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs Keyword Explorer, SEMRush Keyword Magic Tool, Moz Keyword Research can be used for Semantic SEO Research.
- Google Autocomplete, Google People Also Ask, Google Suggested Queries, Google Knowledge Graph, Google Knowledge Panel Semantic can be used for SEO research.
- Resources such as Wikipedia, Wikidata, Wikihow can be used for Semantic SEO Keyword research.
- Youtube Autocomplete, Youtube Video Titles, Comments, Forum Threads, and call center questions or news sources also can be used for Semantic SEO Keyword Research.
- The important point in Semantic SEO Query Research is to group user questions and queries according to specific search intents.
- Google Images and Query Refinement Bubbels also help for Semantic SEO Query Research since they are connected to each other with a contextual hierarchy.
Semantic SEO and Importance of Entities
For Semantic SEO, it is not enough to just use queries that are linked together in a hierarchical order. At the same time, it is necessary to explore the relevant entities and their interconnectedness. Google is able to understand the subject, quality, or depth level of content even based on the context of each entity and the way it connects to other entities. With the way assets are linked, Google can use Contextual Information Retrieval and fill in missing information in the content.
An example of Contextual Information Retrieval is provided below.
“There are 35,000 Museums in the USA. I visited some of them and spent a lot of money.”
In this example, Google or another AI System can estimate that the person spends “US Dollars” in those museums because “spending money” is related to a currency, and Google can rewrite the content as follows.
“There are 35,000 Museums in the US. I visited some of them and spent a lot of US dollars.”
It is important for Semantic SEO that the contents are written clearly and each element is clearly written. Thus, specifying an element and entity more clearly will enable your content to be evaluated faster and with less cost by the Search Engine with Semantic SEO and Semantic Search.
How to Extract Related Entities for Semantic SEO
Finding related entities for a topic is important for Semantic SEO Optimization. You can find entities related to a subject by following the methods below.
- Use Youtube, Bing, Yandex, Google Autocomplete Data.
- Use Youtube, Bing, Yandex, Google Suggested Search Data.
- Use lists of questions like People Also Ask on Google and Bing results pages.
- Scan the latest news on Bing, Yandex, Google to list relevant names, places, laws, currencies, in other words.
- Use Image Search information and query refinement bubbles.
- Discover the relevant entities on Wikipedia via links.
- Follow the Google Knowledge Panel, Knowledge Graph, and “Users Also Searched” suggestions.
- Do research on topics related to the content and do not post content without mastering the subject.
- Use Google Trends and Related Search Trends for specific times to see the connection between entities and sub-topics.
Also, to find the Related Entities, PyTrend can be used. To find out more about PyTrend and how to use it for SEO, you may read our guidelines.
Semantic SEO and Google Hummingbird Algorithm Relation
Google Hummingbird Update was realized in the 15th year of Google in 2013 in order to discover the relationship between different queries and to better read the user intent. Thus, instead of opening a page for each word, many common situations and concepts such as Keyword-stuffing or Keyword-density are a thing of the past, as more organized and comprehensive web pages take the lead in SERP.
Google Hummingbird Update affected 90% of queries. By removing the link between queries, Google Hummingbird has given Google the chance to put queries in a semantic order and analyze the user’s true intent and likely intent. Therefore, Semantic SEO can be said to be a well-established concept for Search Engines from the past. To learn more about Google Hummingbird Update and Effects, read our detailed guidelines.
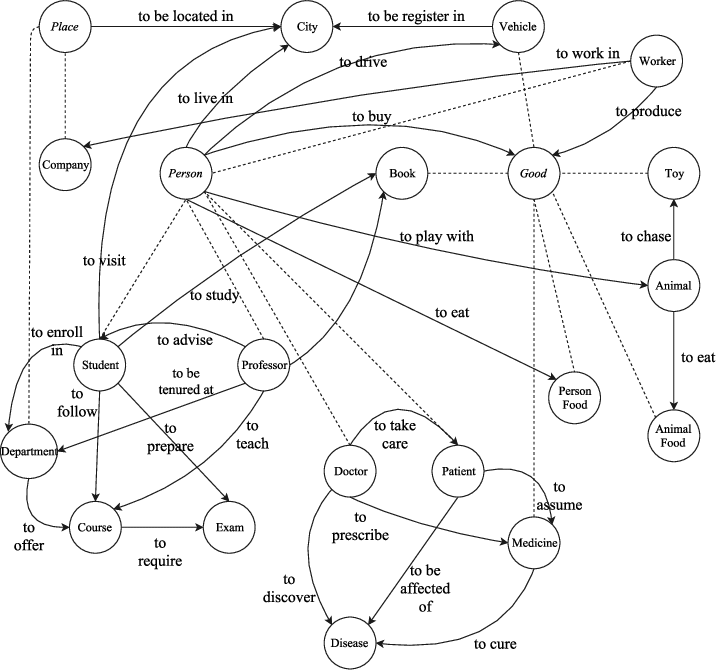
Semantic SEO, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) Relation
Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing are important concepts for SEO. In its algorithms, Google uses AI and Machine Learning to classify queries, make sense of them, link them together, understand page quality, and compare the generated SERPs with each other. Natural Language Processing means interpreting and categorizing content using machines. For this reason, knowing the NLP Methods and knowing the new technologies developed within the scope of NLP methods and Artificial Intelligence will be beneficial in terms of how Semantic SEO can be brought to a better point. When using Natural Language Processing for Semantic SEO, you can perform tests with NLP Models to see if the entities and different phrases in the article are noticeable, whether the article focuses on a subject enough, or the language and emotion structure of the article is enough to meet the industry. You can use it to see if it is suitable.
With NLP, you can see how you can draw the relationships between entities in an article by putting them in a knowledge graph. For more at this point, you can read our “Entity-graph Creation from a Content with Python” guideline.
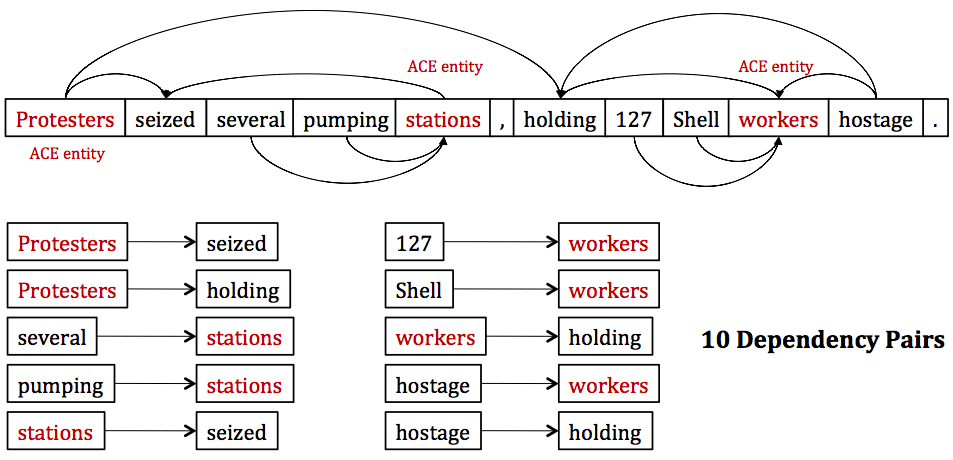
The Relationship of Synonyms and Different Formats of the Queries and TF-IDF Analysis for Semantic SEO
There is a link between Semantic SEO and the different spelling of words, their synonyms. Users can use different words to search for the same topic. It is important to naturally use synonyms or similar words within a topic to satisfy all users within a context, within the context of the relevant search-intent, and to ensure that Search Engine can reconcile difficult concepts. Even if TF-IDF Analysis is not of great importance in SEO studies, it can reflect the approach of different content publishers to a subject. With TF-IDF Analysis, it can be understood in certain criteria which concept or word has greater importance in an article. Different articles that mention the same topic may use different versions of the same concept. It is good for User Experience and Readability to deliver content to users more easily and to explain the same subject to the user with the concepts they prefer to use. Using different variants of the same concept for Search Engines helps algorithms better understand the subject and associate it with specific search intents.
TF-IDF Related contents for better understanding the term.
- To learn what is TF-IDF Analysis, you may read our article.
- To perform a TF-IDF Analysis with Python, you may read our guidelines.
Writing different forms of the keywords will help to get more visibility for different types of search terms and also it will improve the relevance of the content for the subject. While using different forms of keywords, the content’s natural structure and beneficial sides shouldn’t be decreased. Content always should be created for the users rather than Search Engines.
On-page SEO Elements and Semantic SEO
On-page SEO Elements are closely related to Semantic SEO. On-Page elements to be used in the web page can be organized in a Semantic way to better serve the purpose of the content. For example, when conveying a topic, more important questions are answered first, while less sought information can be taken down. This change in the internal structure of the content should be shown in Heading Tags to include the relevant part of the related concept. Words in URLs, Breadcrumb Navigation, Internal Links, Anchor Texts, images in Web Page, alt-tags of images, URLs of images should accompany the relevant subject with the same approach in this context, and harmony should be created in-page items for the certain search-intents and topics.
Elements such as title tags, Meta Descriptions can also be edited in accordance with Semantic SEO. By writing the title and description on the website in a semantic structure, the structure of the content can be understood more easily by the Search Engine and the layout of the website can be understood more easily by the user.
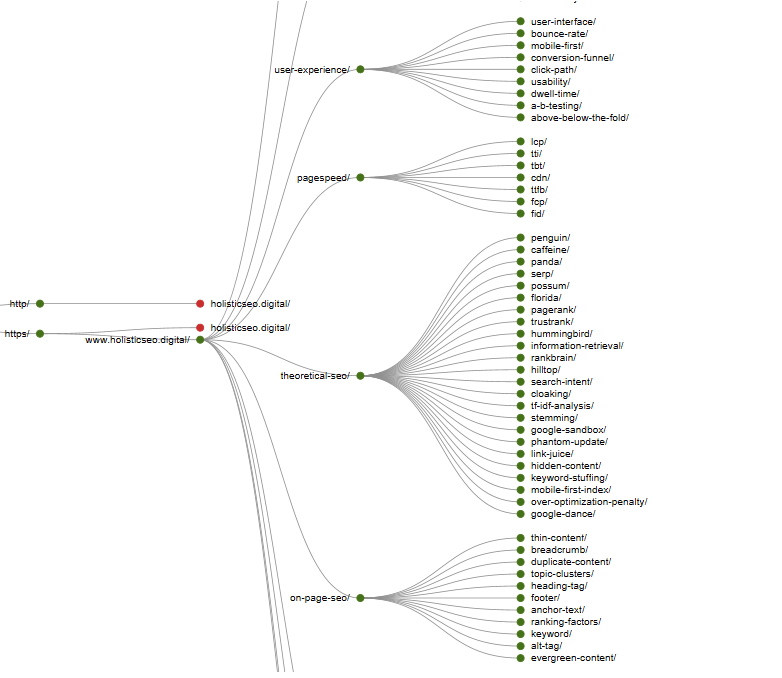
Semantic Site-tree, URL Categorization, and Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO’ya uygun bir Site-tree, URL Kategorizasyonu ve site yapısı oluşturmak, Semantic Search Engine’in web sitesini anlamasını ve onun değerini görmesi için önemlidir. Bu nedenle, içerikleri, ürünleri, hizmetleri farklı search intentlere göre sınıflandırmak, bölümlendirmek ve birbiri ile ilgili iç linkler ile bağlamak önemlidir. Semantic Site-tree hem kullanıcılar için daha temiz ve anlaşılır bir navigation yapısı sunacaktır, hem de Search Engine için tarama, değerlendirme süresini ve maliyetini azaltacak ve farklı arama sorguları ile web sitesinin ilgili bölümünün ilişkilendirilmesi hızını arttıracaktır.
Note: It has been proven that splitting sitemaps into small pieces increases index speed and the number of pages indexed. The main reason for this is those small sitemaps are downloaded more frequently by Search Engines. However, there is no evidence as to whether sitemap categorization contributes to a ranking. However, categorizing your sitemaps semantically in a sitemap index file can make it easier to analyze the coverage report. Semantic compatibility between the Crawl Queue, Internal Site-tree, and the Semantic Sitemap Index file could possibly be a facilitating signal for the Semantic Search Engine.
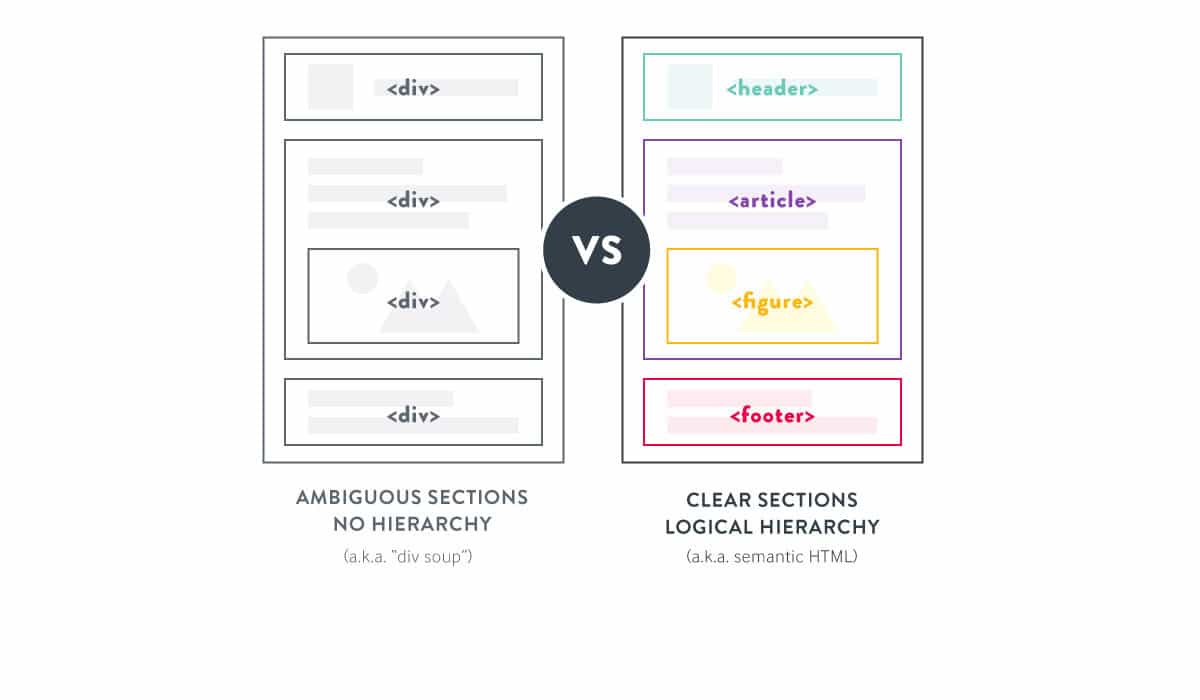
Semantic SEO and Semantic HTML Relation
Semantic HTML is the use of HTML elements that have a meaning in the page DOM structure. With Semantic HTML, parts of a website and web page can be coded according to their functionality. Search Engine Crawlers can recognize Semantic HTML elements and thus, by recognizing the relevant parts of the web page more quickly, it can calculate the rate of meeting search-intents with less cost.
With the use of Semantic HTML, the main purpose of a web page, the main content section, the “Supplementary Content” section with tags like “<aside>”, the author and the areas for navigation can be easily displayed with tags like “<nav>”.
Semantic SEO and Semantic HTML are related. With the use of semantic HTML, the part of a web page related to the search intent can be displayed to the Search Engine much more easily. Consistent and clean HTML code structure and a consistent and clean site-wide design, understandability within the scope of SEO, provides the opportunity to be scanned and evaluated with less cost within the scope of Search Engine Optimization.
As mentioned in the section on Semantic SEO and Featured Snippet, lists, tables, or definition sentences and images can be entered into Featured Snippets. In this context, using a correct HTML structure for lists and tables will be useful for the Search Engine to select the relevant part of the content and interpret it correctly. Thus, it should be said that there is also a link between using Semantic HTML and Featured Snippet Hunting.
You may read our related guidelines for Semantic HTML.
- What is HTML?
- What is Semantic HTML?
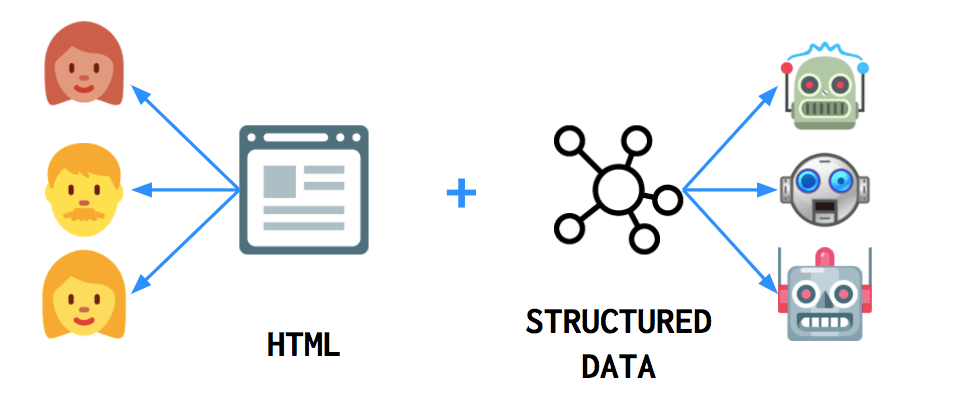
Structured Data and Semantic SEO
Just like Semantic HTML, the use of Structured Data allows URL content to be given to Search Engine Crawlers in a more organized and understandable way. Also, using Structured Data in some cases also creates Rich Results Snippets specific to search queries and search intent.
With the use of Structured Data, what an article is about and the structure of the article, the function, subject, and description of the article or article image, video, or web page can be conveyed easily. Structured Data is the Semantic SEO method, which makes the web page a Semantic structure, making it more understandable for both users and the Search Engine.
Pillar Cluster Content, Content Hub, and Semantic SEO Relation
Pillar Cluster Content is a type of content in which a certain subject is explained with its lower aspects and links to related content pieces in lower units from the relevant points.
Content Hub, on the other hand, is said to be the sum of all related content along with Pillar Cluster Content. Both the Pillar Cluster Content and Content Hub concept are related to Semantic SEO but do not exactly meet the same need. Semantic SEO is an SEO principle in which the concepts of Piller Cluster Content and Content Hub are systematized and defined within a definite need.
People Also Ask, Featured Snippet, and Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO provides a large number of Featured Snippets as it deals with a subject in a language and scope suitable for Featured Snippets. It is also possible to take part in the answers to People Also Ask questions under Semantic SEO. For the most part, Featured Snippets are around 40 words and 320 characters. Therefore, when writing “Semantic Questions” such as “Who, When, How Much, Where, How” and their answers within the scope of Semantic SEO, attention should be paid to the letter and word constraints in paragraphs that can acquire featured snippets. By doing experiments on Google and Bing Featured Snippets, new letter and word limits can be checked after updates.
Another issue is the types of Featured Snippets. Featured Snippets can include lists, tables, or direct definition sentences and related visuals. Therefore, while making sure that the relevant entities are mentioned in these sentences, within the scope of Semantic SEO, content editing should be prepared in accordance with these rules and structures.
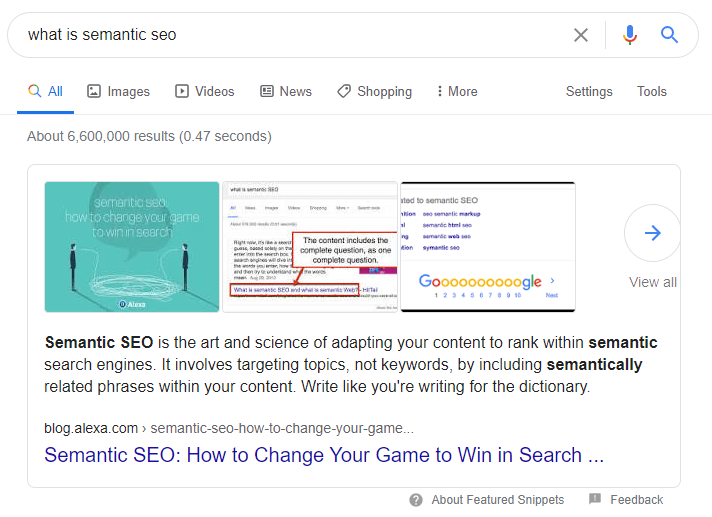
In order to be included in the Featured Snippet, in the Semantic SEO Scope, “heading tags”, that is, “question type sentences” in article titles, should be used, while there should be scientific information sentences containing broad-time expertise in the paragraph. Google SERP features such as People Also Ask and Featured Snippet is used to greatly improve the Semantic Search experience. Organizing the information on the Internet and organizing the SERP and the content publisher organizing its own website and content structure are interrelated.
Semantic SEO methods and understanding should be used to take place in Featured Snippet and People Also Ask sections, which are Semantic Search Results Page elements.
What is the Difference between Semantic Search and Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is related to the Search Experience Optimization and Search Engine Optimization terms. Semantic SEO is being performed by the Search Engine Optimization Experts. On the other hand, Semantic Search is a part of the Search Engine Results Page design, content, and functions. It is being performed by Search Engine Creators, Designers, and Programmers.
To learn more about Semantic Search, you can read our related guidelines.
Final Thoughts on Semantic SEO and Holistic SEO
Semantic SEO is not just about creating a “content strategy” for a Holistic SEO. The semantic concept is present at every point of our lives. Due to human nature, they understand and make sense of every element in the semantic structure. Man-made algorithms also make sense of the elements in a semantic structure faster and with less cost. Semantic SEO, as a thinking system, increases the critical and analytical thinking power by showing the interconnection of concepts for Holistic SEO and improves the Search Engine Understanding ability. Algorithms are further divided into “Creative” and “Semantic”. “Semantic algorithms” are designed to detect patterns that progress in certain patterns and to extract the differences between them. “Creative algorithms” are designed to create different patterns on these differences. Most Google and other Search Engines use Semantic Algorithms that can see Pattern-based differences.
In this context, Semantic SEO and Holistic SEO have closely linked concepts. Semantic SEO guidelines will be furthered by us.
- Sliding Window - August 12, 2024
- B2P Marketing: How it Works, Benefits, and Strategies - April 26, 2024
- SEO for Casino Websites: A SEO Case Study for the Bet and Gamble Industry - February 5, 2024


Hi
I want to let you know that the paragraph “Semantic Site-tree, URL Categorization, and Semantic SEO” is not in English. It’s written in Turkish.
Thank you for the great effort you are putting into your articles to make us understand SEO better.
Thank you, Abdallah but it is still an SEO test for me.
Koray, did you mean for us to translate – Semantic Site-tree, URL Categorization, and Semantic SEO- ? I’m not sure what you meant when you said it’s still an SEO test for me?
Seems Yasunori Abe copied the Turkish content you included… 😅 as you can see here https://www.osusume-co.com/semantic/
Thanks for this, I need to add a link to it on a blog of ours!
Hello Gabriella,
I tried and am trying to see how Google chooses the primary language of a web document. Google might show some Turkish queries just because of a few Turkish paragraphs, or they require more Turkish paragraphs. Maybe, if I search from Turkey for the specific topic in English, since a certain portion of the document is Turkish, it might help for further audience matching. It is a little about semantics too. Because, semantics are language agnostic. Thus, even if it s a UX issue, from semantics’ point of view, still it can have a proper connectedness. I am trying to see some thresholds and possible reflexes from the search engine. They might also ignore these types of language inconsistencies, if it is not more than certain %. They always have a threshold for further decsions. Thank you, I am happy to see you in our website.
really helpfull Koray thank you please publish more
Thank you for your kind words, Ali.
Impressive 👍 I’ve watched this post 7 days ago in the 2 page on serps , now it’s #2 in the first page below brayn Dean.
The best article on semantic seo 🤗
Thank you so much, Alparslan.
Awesome 👍 guide mate, it’s one of the best guides I ever found on the internet.
Thank you, Suraj!
Amazing article indeed. Thank you Koray for that.
Do you think programs such as Surfer and Yoast test successfully if the content is sematic friendly?
Thanks again
Love and respect brother
No, not necessarily. Semantics are dynamic.
I’ve learned so-called advance on-page and content writing + optimization in a very single post. So many nuggets you shared with us Koray. Thanks.
Thank you for your sincere comment for our guide on Semantic SEO dear Hayat Ahmad. It means a lot to us.
Thanks for the amazing content. I don’t understand the HTML and SSEO part. DO I need programing knowledge to understand that?
Hey MD Redoy Rahmam,
No, you do not need programming knowledge for the Semantic SEO, or Semantic HTML, or their intersection. You should know the definitions and meanings of the Semantic HTML tags to connect them to the Search Engine Optimizaiton context, it is good enough.
Excellent article how many articles does a site need for semantics to work does the (DA) matter or just semantics?
Dear James,
We sincerely appreciate your thoughtful comment and the Holistic SEO Team is truly gratified by your interest.
The required volume of articles substantially depends on the specific industry as well as the historical data and performance metrics of a given website. Each field presents its own unique requirements, influenced by various factors such as competition, audience demand, and the complexity of the topic. For instance, while an industry like pet care might necessitate a high number of articles due to its broad scope, a niche industry may require fewer but more in-depth articles.
Regarding your query about “telescopes”, an estimation might be around 300 articles, accounting for a comprehensive coverage of the topic. However, when it comes to a burgeoning and wide-ranging sector such as electric cars, even 4,000 articles might not suffice to capture the entire spectrum of information, given the rapid advancements and evolving consumer interests in this field.
Please note that these are approximations and the optimal volume of content varies significantly based on a multitude of factors including the specific nature of the business, the target audience, and current market trends.
Thank you once again for your comment and for contributing to our ongoing discussion on this matter. We are here to provide authoritative and data-driven insights to serve the SEO community better.
It’s the best article on Semantic SEO on the internet. I had a question, for example, if my site is about Restaurants in the UK and let’s suppose I’m writing about McDonald’s menu. Do I have to cover all the related entities in the UK only? Or I have to cover general ones also that may or may not be valid to McDonald’s UK.
Hello, Arnav Gupta,
Thank you for your kind words.
If you have a restaurant in the UK, you should process the “restaurant” related contexts inside the UK, whether it is a locale, or the food-service.
But the things that you cover always should have a contextual connection.
Absolutely impressed with the introduction to Semantics SEO. As someone with a programming background who’s recently deived into SEO, this has opened up a whole new avenue for me to investigate. Thank you, Koray kardeş.
Thank you, Muhammad!
I have little bit confusion about relation Picture in the Hummingbird Algorithm Section or You Just Write the actual Sentence in the caption so it helps us to understand how google make relationship between words. The Whole Article is too good and Full with Premium Information.
Thank you, Faiz!
Thank you for this very complete and detailed article about Semantic SEO. I’m wondering, the majority of Search Queries on my site clearly show that the user’s Search Intent is about purchasing a specific Canvas Printing product. Can I apply Semantic SEO to such Search Queries and Search Intents?
PS: Sorry if there is something unclear in the wording. I come from Vietnam. I’m using Google Translate for the above content.
So, I have started to learn Koray’s framework from today 🙂 Will be finishing all of his website content in the next 3months. Just completed this and I am amazed to learn a lot of new stuff. Let’s see how far I can go.
Thanks for this detail article
Thank u so much sir for the wonderful knowledge i always enjoy your framework or case studies like i m reading a wonderful story 😁 as an engineer i deeply learning and understanding the concept and i m your indirect student and fan of your work and also helping my Asian community so they learn this ammzing concept making video plus post if very easy to understand concept so they can understand
Regards Ehsan Semantic SEOs
The wonderful insights you’ve explained step by step are truly impressive. I’m surprised some people still don’t grasp the concepts, as the knowledge you’ve shared is both thorough and profound. Hats off to you sir
Great read! This post breaks down Semantic SEO in a simple, easy-to-understand
The Section “Semantic Site-tree, URL Categorization, and Semantic SEO” is in turkish
Do you do consultation for solopreneurs? Also recovery from google updates?
Yes, we do provide these services. Send an email to the [email protected].
Impressive Content, Thanks for sharing This Informational Blog about SEO.