SERP is the abbreviation of “Search Engine Result Page” and refers to the search results page after entering a keyword in a search engine. The order of the search results is crucial for search engine optimization. The first page of the SERPs is often referred to as “Top10”. Every result on the SERP is ordered in descending order in terms of quality, relevance, and trust.
The ranking in the SERPs is essential for the success of websites. Website operators want their offers to be displayed as high as possible in the SERPs. According to studies, the majority of clicks are distributed over the first 10 search results for a keyword. After the first SERP, the user’s attention drops drastically. According to a recent study by Brian Dean only around 1 percent of the clicks on the second Google results page are accounted for. The order of the search results in the SERPs is determined by the secret algorithms of the search engines. According to the search engine Google, over 200 factors are included in the ranking of a website. These include, for example, qualitative links that point to a website, as well as user-relevant, high-quality content on a website.
SERP Features Based on Query Intent and SERP Interaction with User
The representation of the SERPs varies depending on the search query. Depending on the search term entered (keyword or keyword combination), advertising, images, results from Google Maps, and/or ratings can be displayed in the search results. In addition, the SERPs can vary depending on the user, because they are personalized according to location and search history. However, if a user feels that the displayed search results violate their personal rights, it is possible to request that the search results be removed by Google. Because a high ranking position is so important for the traffic of a website, search engine optimization (SEO) tries to positively influence the position of a website in the SERPs. Experienced SEOs, for example, analyze users’ search queries for specific terms and try to answer them in the contributions of a website.
The decisive factor for the ranking of a website in the SERPs is above all how relevant a website is for a specific search query. So that search engines can better scan the content of a website, it is important that the website content contains relevant keywords on the topic. As Google recognizes semantic connections better and better, a website should not only be optimized for a certain keyword, but for an entire topic environment – for example by integrating relevant terms and synonyms. With regular updates such as Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird, Google has refined its algorithm to show users more relevant results for a search query.
With the Google updates, the SERPs have also changed. Google has expanded the so-called Knowledge Graph with its Hummingbird update. This means that certain search queries in the SERPs are already answered completely so that users no longer have to click on individual search results. Successful search engine optimizers must always be up to date with the latest Google updates and adapt their SEO strategies accordingly. However, if an attempt is made to influence the search engine ranking using unfair methods and tricks such as keyword stuffing, Google penalizes the corresponding website. This has a negative impact on the ranking and can even lead to complete exclusion from the index.
Another way to get the user’s attention in the SERPs is through search engine advertising (SEA). Google Adwords ads are displayed above the search results and to the right of them on the SERP. Most companies use a combination of SEO and SEA to drive traffic to their website.
Building SERP Snippets
According to the studies, the user views the SERP in just 1.17 seconds on average. For this reason, the SERP snippets play an essential role.
These snippets, the text of the respective search result, consist of a headline (title) and a description text (meta description). The text can be maintained by website operators in the metadata of the content management system (CMS). The metadata strongly influences whether the user clicks on a specific search result of the SERP or not. Therefore, the title and description should be as meaningful as possible. The sensible placement of relevant keywords in title and description can also have a positive effect on the ranking. However, the associated website should always do what it promises.
When formulating the SERP snippets, it is important to get to the point precisely. Google only allows a certain number of characters: A rough rule of thumb for the meta description is that it should not be longer than 150-160 characters including spaces. The title is all about the width in pixels. However, it should not exceed 70 characters. A helpful tool that shows how the snippet appears from the user’s perspective is the SERP Snippet Generator from Technical SEO platforms.
Some of other related articles for the SERP Term and its analyse usage:
- What is User-retention Rate?
- What is Conversion Funnel?
- What is a Mobile-first Design?
- What is Click Path?
Eye-tracking Experiments by Search Engines on SERP
The main income resource of the Search Engines is of course the Search Engine Advertising revenue. If a Search Engine can’t understand the eye-tracking data on its own SERP, it can’t create enough revenue. Because of this situation, Search Engines change their paid search results’ snippets with regular experiments. Most of the Search Engine updates are being done in SERP Design such as background color or title, description length. Most of these updates serve to the purpose of creating the most interactive Search Engine Results Page. The average length of stay for SERP is only 50 seconds. Google works as a user redirector and reference for information source along with being an information organization like other Search Engines. But, also Search Engines tries to create more interactive user experience with themselves, that’s why they give answers on the SERP. Also, mainly Google is creating an ambient optimization process with a wider vision thanks to Android Phones, Youtube, Gmail, Google Assistant, and more.
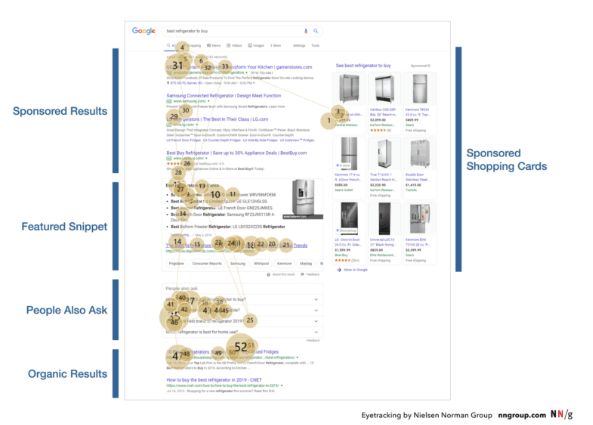
Designing SERP in a better way is one of the main purposes of the Search Engine for creating more revenue and engagement via the searchers.
Click Rate Differences According to the Position on SERP
The position of a search result in the SERPs is immensely important for search engine optimization. For example, only about 5% – 10% (depending on the study) of all users click on the second page of the SERPs, which means they rank 11-20.
First place accounts for 30% -40% of all clicks, second place gets around 15%, third and fourth places have 10% and 7%, respectively. Depending on the data available in the study, these values may fluctuate slightly, but the trend has remained constant over the years.
Top3, Top5, Top10, Top100 Terms for SERP
Terms such as “Top 3”, “Top 5”, “Top 10” or “Top 100” are often used to make certain values of search engine optimization clear.
Originally the first page of the SERPs was the “Top10”. In the meantime, Google has adjusted the SERPs several times, so that depending on the keyword only “Top7” or “Top8” can be spoken of. E.g. some keywords have up to 3 AdWords ads, which are not actually classified as SERPs. Local search queries can result in a local business directory in the SERPs, which represents an almost independent positioning.
Since the top 3 are clicked on most often, positioning them promises maximum traffic in relation to the search volume of the respective keyword.
If a result is in the Top 100, it is said that the respective landing page “ranks” – that is, the crawler has included it in the index .
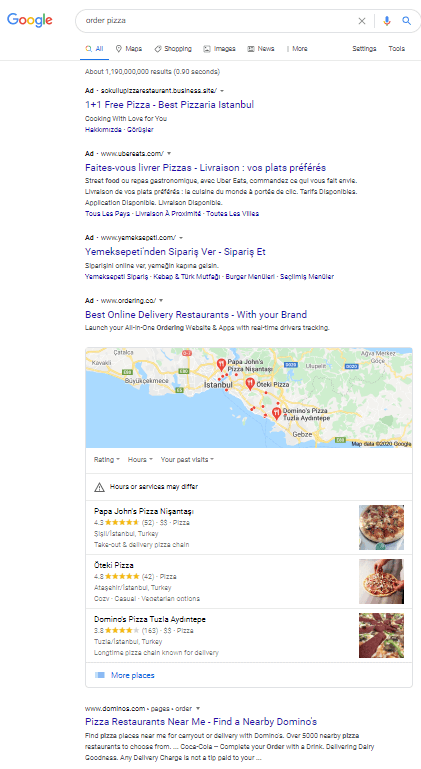
Rich Snippets
The search results can be enriched with so-called “snippets” or “rich snippets”. The goal is to motivate the user to click on the result. Different techniques, such as a promising meta description, or prominent characters such as ticks or smileys (UTF8):
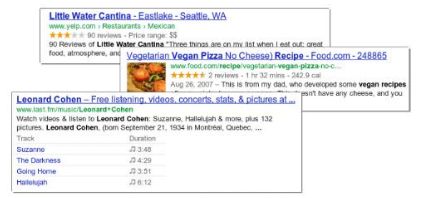
SERP Design Depends on Many Factors
While the SERPs at the beginning of Google search in the early 2000s were still relatively static and the same for almost all users within a country version of the Google search engine, the search results today depend on many different factors. On the one hand, different ranking factors still determine the placement of individual snippets. In addition, there are other signals that affect the order of the results:
- Registered users: If a Google user is logged in with their account, the search results will be adapted to their previous use, provided that their privacy settings allow this modification.
- Browser history: If a user does not clear the cache of their browser, Google receives information about previous search queries via a cookie and adjusts the results accordingly.
- Location: If geolocation is activated, Google adjusts the SERPs to the respective location of the user. For example, the search results for the search term “Pizza Lieferdienst” look different in Berlin than in Munich. For local search results, results from Google Maps are also increasingly integrated. In addition to geolocation, Google also uses pointers in the search query to provide search results that match the user location.
- Device: If a user does a search on a mobile device, the search results will usually be different, since Google, for example, prefers mobile-optimized websites in the SERPs for smartphones.
Last Thoughts on SERP and Holistic SEO
As high as possible – this is the motto of website owners when it comes to positioning in the SERPs. Because most clicks are on the first search results page on Google. Search engine optimization tries to influence the ranking of a website in the SERPs. In addition, search engine advertising such as GoogleAdwords serves to draw users’ attention to their own website. In addition, the design of the SERP snippets plays an important role when it comes to generating clicks in the SERPs. With the Google updates, the SERPs have changed. Instead of plain text, users are now also presented with images, videos, ratings, and maps in the search results. Successful search engine optimizers must always be up to date with the latest Google updates and adjust their strategies accordingly.
If we think with a Holistic SEO vision, SERP will only go beyond a certain definition or view. Every update that Search Engine performs in SERP is an opportunity to understand Search Engine. If Google expires a snippet type that it thinks is not getting enough clicks, you might consider removing a similar design.
A Holistic SEO can easily understand the canonical (main) intent owned by a query via SERP Design and Layout. If image-pack or map results are at the top, the query’s local sensitivity or visual necessity is high. In this case, the current subject can be targeted from social media accounts, GMB, local directories, Pinterest, as well as these points are also taken into account for the content to be created.
Holistic SEO is not just the person who examines SERP. He is also the person who triggers different SERP features by combining various points semantically. This can sometimes be Knowledge Graph, Knowledge Panel, Featured Snippet, Twitter Carousel, Youtube Carousel for a client. It is possible to trigger a Featured Snippet, which was not previously available, by simply examining the SERPs available for the same topic in different languages. Most SERP Features are features of the Entity-based Search Engine. That is, it is language independent.
Therefore, it would be beneficial to approach SERP by thinking with a wider angle. Soon, our SERP Guideline will be further elaborated with this perspective.
- B2P Marketing: How it Works, Benefits, and Strategies - April 26, 2024
- SEO for Casino Websites: A SEO Case Study for the Bet and Gamble Industry - February 5, 2024
- Semantic HTML Elements and Tags - January 15, 2024


