Search intent is the name for the motivation of the searcher, for example when entering a query into a search engine. Google and other search engines evaluate the hits found in terms of content and evaluate how well they match the suspected search intent. The better this fit between the information on a website and the entered user intent or search query, the better the page ranks in the search results from Google. Sometimes one speaks of search intent with user intent.
What Types of User Intent (search queries) are There?
Google assumes that every searcher wants to solve a problem by entering a search in the search engine field. These types of search queries or user-intent have been roughly divided into the following categories.
- Informational Queries
- Transactional Queries
- Commercial Queries
- Navigational Queries
- Brand Queries
- News Queries
- Local Queries
1.Informational queries:
These are usually individual terms that you would like to have explained, a process or activity that you may have explained. An informative query would be, for example: “How do I grow tomatoes on the balcony?”, “Hinkelsteinfertigung”
2.Transactional queries:
These are requests that hope to interact, video on a topic, a download, etc. Example of transactional user intent: “Tips kettle cleaning, download checklist SEO”
3.Commercial queries:
These are inquiries that should result in a purchase or a (presumably) chargeable service. Example of a commercial user intent: “Buy tricycle, support online marketing, buy plants, buy product xy cheap”
These are search queries that indicate that the searcher would like to go to a certain website or portal and possibly to a certain content there. Example of searches with navigational user intent: “HolisticSEO blog, youtube cat videos, facebook person xy”
5.Brand queries:
This type of query is the specific query of brand names or company names or services). Example of trademark inquiries: “SEO Kitchen, Mc Donalds”
6.News queries:
This type of request is primarily intended to produce current results, such as the latest reports on a specific topic, person or event. Example of news queries: “Company X share price, gold price, Donald Trump, Corona”
7.Local queries:
The intent of these searches is clearly local. If a local query is recognized, the search results are not only aligned according to the accuracy of fit but also local proximity. This is particularly the case if the request is made from a smartphone. Example of local searches: “Nearby restaurants, dermatologist Cologne, lawyer Munich
New Classification Methodology of Google according to User and Search Intent
This type of subtle subdivision is the conventional pattern of differentiating search queries in search engine optimization. In fact, Google itself informed in March 2019 that the company differentiates between “DO” “KNOW” (“KNOW SIMPLE”) “VISIT IN PERSON” and “WEBSITE” queries and evaluates the results for search queries for all keywords accordingly.
- “DO” stands for specific actions such as buying, installing, or downloading. The first results that you get on such inquiries are unfortunately not particularly easy to achieve through search engine optimization since these are paid advertisements, shopping entries, or the like.
- “VISIT IN PERSON” are inquiries aimed at actually visiting the business or company in the near future. Therefore, results are played here that help to find the location searched for with the keyword. Important: Of course, Google’s own smartphone-related results are played out particularly prominently. This can be entries on Google Maps and the like.
- “WEBSITE inquiries”, however, focus on the content of specific websites, portals or the like. Here you can align your own strategy with the relevant keywords.
- “KNOW” requests are about information. That is why direct responses from the search engine, such as featured snippets, are included here. Because in the category “KNOW” there is still the special form “KNOW SIMPLE”. Questions about keywords and facts are already answered in the SERPS on Google. Examples of this could be questions about simple factual knowledge such as “How high is the Empire States Building” or “What is the capital of Belgium?” For more in-depth questions that are not so easy to answer, search engine optimization has very good chances of placing the website with comprehensive answers and knowledge.
Why is the Search and User Intent one of the most important Ranking Factors?
The declared goal of search engines, especially Google, is always to present the perfectly fitting result for the search query. Therefore, the search engine tries to create even better search results with user intent. It is about creating measurable factors as to when a search query actually matches a corresponding website, not just keyword-based, but also suitable for the user’s information needs.
Google and Bing can create personalized Search Engine Results Page according to the users’ past search activities and browser data.
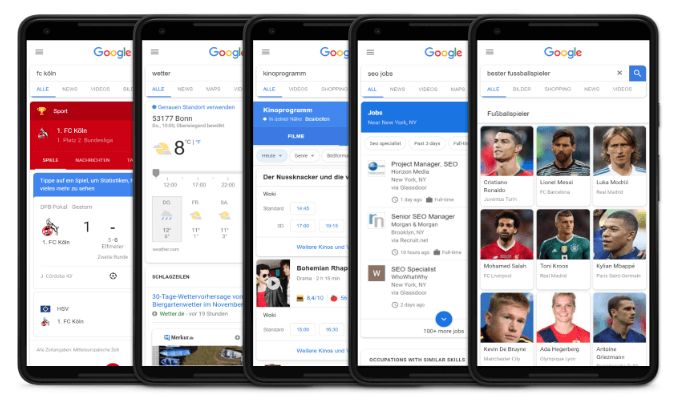
Through the user intent in combination with the appropriate keywords, Google and other search engines can better match what the user was really looking for with his input. The behavior of the user on the page presented is then incorporated into further rankings.
Search Engine Results Page Design can clearly show you to the identity of a query along with different search intents’ harmonies in that query.
For website owners, this means that content on the website should be created and aligned so that it corresponds to the user intent. What kind of content does the customer want to be presented if he chose this keyword when searching? There are big differences in the user intent, which the search engine crawlers also recognize. As a content publisher, you can only achieve good rankings if your content, page structure, and functionality are geared towards user intent.
Google’s Future Purposes on Search Intent
With a company of the size and influence of Google, there is public communication in many places. Google therefore regularly provides insight into its goals. For example, Ben Gomes, the ex VP Search at Google, explained in a blog post last year the goals for the next 20 years of Google search. But many other documents and publications also provide an impression of Google’s thinking. For SEOs, the Google Quality Rater Guidelines are the most important document: Google describes his view of ideal search results and has an army of freelance employees regularly measure the current SERPs against this standard. What better idea of Google’s goals could we get?

User Intent ”(point 12.7, page 68) Google describes in the Quality Rater Guidelines which user/search intents there are and which answers Google would like to give to them. The concept of user intent is not new: user intention in information retrieval systems has been observed for many decades. There are also early adaptations in the web search, such as in this paper by Andrei Broder, who worked at Altavista. Some of the other Search Intent and User Experience Related Articles:
- Breadcrumb Navigation for Similar User Intents
- Conversion Rate Optimization with Conversion Funnel
- Mobile-first Design for Mobile User’s Behavior Patterns
- Click Path Design for User Intent
- Eye-tracking for UX
- Heading Optimization for Scannable Content
- Search Engine Result Page
User intent: What does the User Want to Achieve with his Search Query?
An example: If a searcher enters “house” as the search word, it is so unspecific that the search engine could probably display several million different results. But each addition makes the search query clearer: “House cleaning tips”, “Building a house in Long Island”, “Renovating a house”, “House fireplace XY”, “Renting a house on the island of Hawai”. Searchers usually enter specific questions or phrases into the field of the search engine so that the user intent can clearly identify the problem to be solved. User intent therefore clearly shows what type of information and presentation the visitor is expecting. Depending on the search entered, the user would like to buy, find a specific place or page (on the web), get information or, for example, receive current information. Google assigns the entered term or phrase to the respective search intent. The search results are correspondingly different.
Why is the User Intent Important for SEO?
If you as a website owner want to be found for certain content or intent, you have to provide the corresponding content on the website. This comparison ensures that Google evaluates your website or individual page as relevant for a specific search query and then shows it accordingly in the results. In addition, the behavior of your visitors on the website will be correspondingly more positive if you are presented with suitable content depending on your own search query. This in turn leads to a longer stay on your website, more clicks, and more positive behavior, which in turn turns out to be positive for the evaluation of your page by Google.
How does user intent influence keyword research?
If a website operator wants to be found, he should know the user’s intent of his visitors and fulfill the respective information need as best as possible. For keyword research, this also means that you look closely at which searches are made by which audience. Finally, based on this investigation, you can then do specific keyword research. In this way, you get not only relevant content for the user, but also long-term content, which the search engine and even more importantly the users will rate well.
Does Google need your website?
Now we come to the key question that you have to ask yourself for each keyword or keyword cluster: Does Google need your specific website to fulfill the search intent? For organic rankings, the answer to this question for the intention visit-in-person and Do will often be negative. Visit-in-person is dominated by Google Maps integration. Organic rankings can only be found in the significantly less clickable area below the box. It tends to look even worse for the results of Do-Intention, which are blocked with advertisements. Google will have to step up its monitoring efforts to generate growth. For know intentions, the answer is twofold: If it is a question of very simple answers that Google can answer as know-simple directly in the SERPs, this will increasingly happen. However, if you answer complex questions and topics with your content, it will still work organically in a few years.
Search Intent and User Intent are important terms for SEO. Holistic SEOs can change the layout of their web pages according to the Main Intent and Subintents to satisfy different user personas with a lesser page amount. This will create authoritative web pages in a certain Knowledge Domain. Search Engine doesn’t need your web site to satisfy searchers, but you need to prove that your service, product, function, and information satisfy the user. So, Google may trust your web site in time for certain queries and topics.
As Holistic SEOs, we will continue to refresh our Search Intent article to perform better in our SEO Projects.
- Sliding Window - August 12, 2024
- B2P Marketing: How it Works, Benefits, and Strategies - April 26, 2024
- SEO for Casino Websites: A SEO Case Study for the Bet and Gamble Industry - February 5, 2024